我校在建立葫芦科嫁接发根体】系用于鉴定砧穗互作可移动信号研究中取得新进ξ 展
南湖〇新闻网讯(通讯员 耿守玉 杨丽)近日,我校园艺植物生物学教育部重点实验室、园艺林学学院别之龙教授课题组在葫芦科作物发根体系和砧穗互作方面的研究成果以“An efficient root transformation system for CRISPR/Cas9-based analyses of shoot–root communication in cucurbit crops”为题在Horticulture Research发表。
葫芦科作物,包括黄瓜、南瓜、苦瓜、丝瓜、瓠瓜、西瓜、甜瓜等,是重要的︼瓜果类蔬菜。嫁接是一种古老的农艺手段,历史悠久,沿用至今,仍然在园艺作物生产中广泛使用。南瓜对枯萎病等土传病害的抗性强,是其他葫芦科作物的常用砧木》》。葫芦科作物由于易嫁接、容易获取木质部和韧皮部液等特点,也是研究植物地上和地下长距离信号的良好模型。以往以葫芦科作物▅为对象,采用组学手段发现了大量可长距离运输的信号物质,然而由于大多数葫芦科植物缺乏高效的转基因╱体系,限制了相关基因的功能验证和机制解析。因此,开发适合葫芦科植物的相关基因功能验证体系尤为重要。
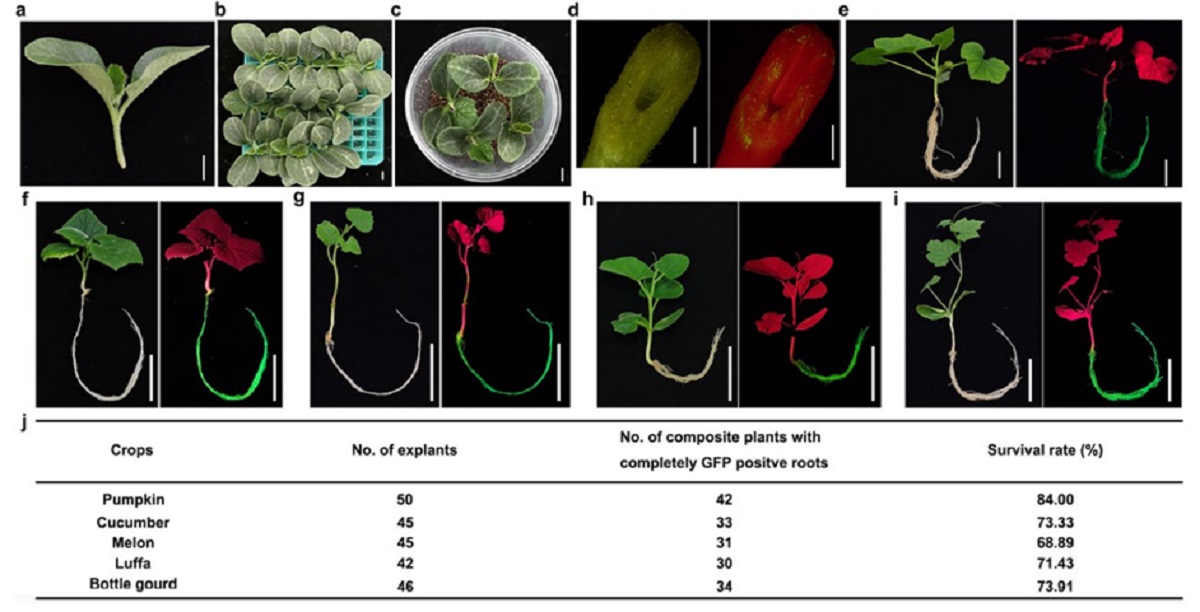

图1 葫芦』科发根体系
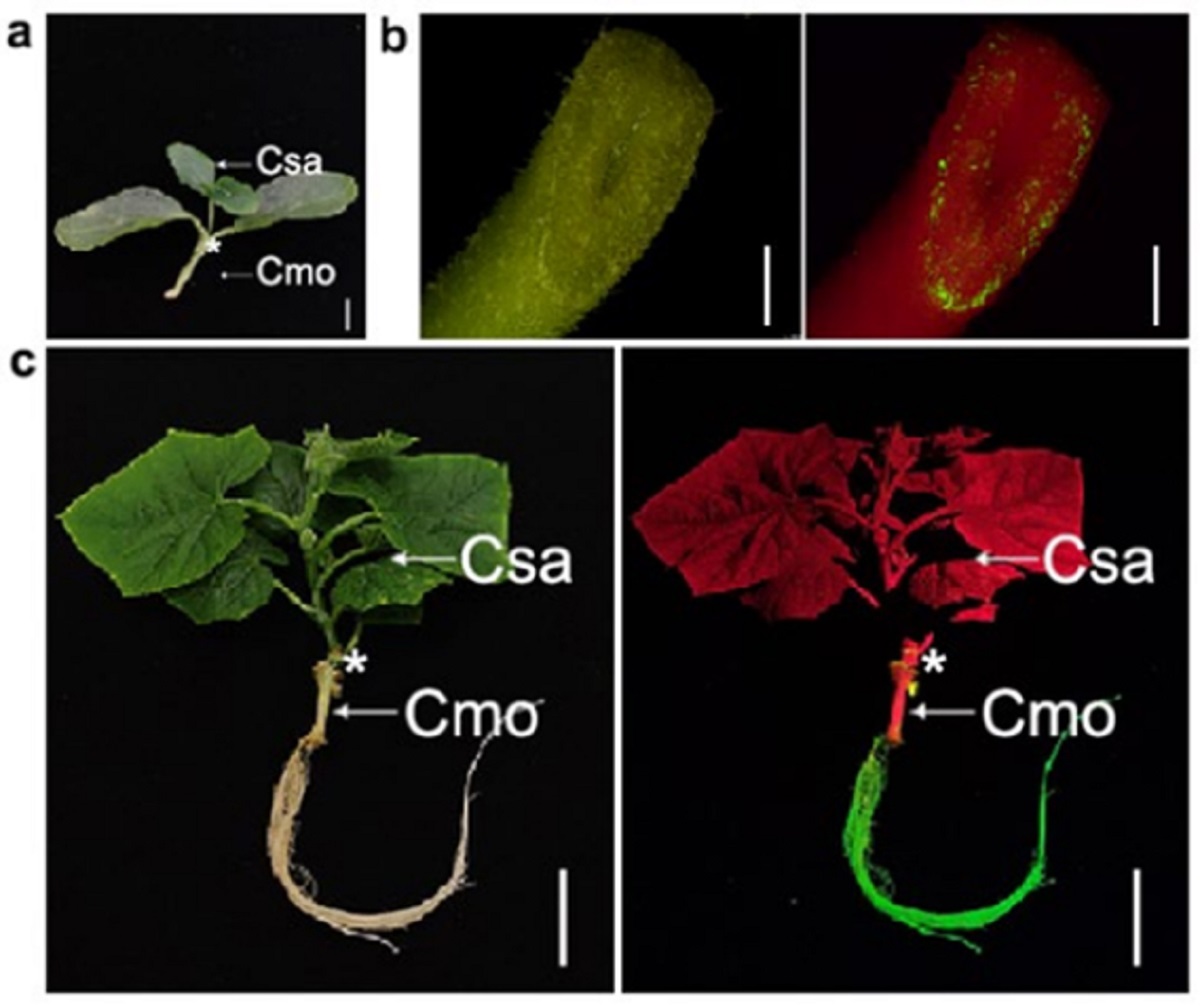
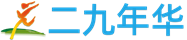
图2黄瓜南瓜嫁接发根体系
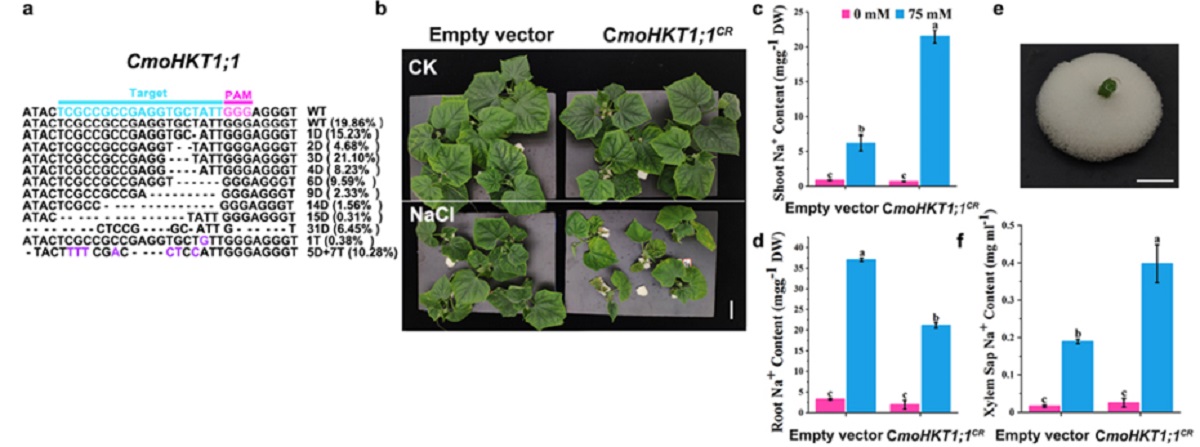
图3黄瓜南瓜嫁→接复合体根系敲除CmoHKT1;1后表型鉴定及离子测定
图4南瓜和黄瓜发根体系超表达CmoNHX4亚细胞』定位及离子测定
该研究采用农杆菌侵染带有生长点的外植体,首先建立了一种适宜葫芦科作物的发根体系,在南瓜中的效率可以达到84%,该体系同样适用于黄〓瓜、甜瓜、丝瓜和葫芦等葫芦科作物(图1)。另外,研究者还将发根体系的方法与△嫁接方法进行了组合,可以在发根的同时进行嫁接,以实现对砧木的遗传改∮造(图2)。进一步,该研究在∏黄瓜/南瓜嫁接复合体中对CmoHKT1;1进行了基因编辑,相关机制▲研究表明CmoHKT1;1通过限制Na+的长距离运输参与南瓜砧木提高黄瓜接穗的◣耐盐性(图3)。另外,将南瓜Na+/H+逆向转运蛋白CmoNHX4超表达在黄瓜根系中能显著提高黄瓜的耐盐性(图4)。该发根↓体系同样适用于在根系细胞中进行亚细胞定位和对根系进行荧光染料染色观察等细胞生物学实验(图4)。以上研究建立了适合葫芦科不同嫁接组合的根系瞬时转化〓系统,并将其№成功应用于瓜类耐盐基因的功能验证,为研究葫芦科作物根系基因功能及砧穗互作提供了一种有效方法。
我校园艺林学学院硕士研究生耿守玉、博士研究卐生Hamza Sohail和博士→研究生曹海顺为论文共同第一作者,我校园艺植物生物学教育部重点实验室别之龙教授和杨丽副教授为共同通讯◇作者▼。本研究得到国家重点研发计划、国家自然科学↑基金、湖北省自然科学基金创新群体、中央高校基本科研专项资金和国家西甜瓜产业技术体系等项目的资助。
审核人:别之龙
【英文摘要】
Cucurbit crops are suitable models for studying long-distance signaling in horticultural plants. Although thousands of substances are graft transmissible in cucurbits, functional studies have been hampered by the lack of efficient genetic transformation systems. Here, we report a convenient and efficient root transformation method for several cucurbit crops that will facilitate studies of functional genes and shoot–root crosstalk. We obtained healthy plants with completely transformed roots and non-transgenic shoots within 6 weeks. Furthermore, we combined this root transformation method with grafting, which allowed for gene manipulation in the rootstock. We validated our system by exploring salt tolerance mechanisms using a cucumber (Cucumis sativus)/pumpkin (Cucurbita moschata Duch.) (scion/rootstock) graft in which the sodium transporter gene High-affinity K+ transporter1 (CmoHKT1;1) was edited in the pumpkin rootstock, and by overexpressing the pumpkin tonoplast Na+/H+ antiporter gene Sodium hydrogen exchanger4 (CmoNHX4) in cucumber roots.
论文链接:https://academic.oup.com/hr/advance-article/doi/10.1093/hr/uhab082/6511825?searchresult=1
未经〗允许不得转载:二九年华大学门户 » 我校在建ぷ立葫芦科嫁接发根体系用于鉴定砧穗互作可移动信号研究中取得新进∏展
相关推荐
- 高⊙等教育评估专家瞿振元、王战军◤来校调研
- 【战“疫”快报】公共管理学院师生为社区防疫工作建言献策
- 我校获湖北发展研究奖一等奖
- 中央歌剧院为华中农业∞大学开设的“空中艺术讲①堂”圆满落幕
- 长江经济带大宗水生生物产业绿色发展教育部工程研究中心2021年建设任务研讨会举行々
- 郭刚奇带队赴建始县调♀研挂职干部推进定点扶贫工作
- 一个创意想法是如何实现的
- 西藏农牧学院党委副书记、院长娄源Ψ冰一行来校考察
- 第二届中俄生物信息学☉和计算生物学研讨会∴在我校举行
- 校长李召虎春季开学寄语同学
- 跨年狂欢会:师生〖同台演绎 精彩汇聚狮山
- 马克思主义学院专题学习习近平总书记系列最新重要讲话精神
- 本科生先进集体与个人分享交¤流周首场〖活动举行
- 学校专题研究部署落实教育⌒ 部2020年“二上”预算 布置会议精神
- 阅读接力:在分享中感悟阅读魅力
- 工学院召开∩2020年暑期事业发展研█讨会暨科研团队建设与发展交流会
- 彭健教授和蒋思文教授团队发表动物脂肪发育调控机制的综述论文
- Animal Diseases召开2021年度编ω委会
- “爸妈,我在华农过年〗挺好的!”
- 学校2021年度教职工健康体检如期开展
新闻公告
- 农业微生物学国家重点实验室召开发展研讨会 01-29
- 奉献有你,温暖有我:我校返乡学子开展寒假志愿服务 01-28
- 我校学子前往神农架科创中心开展科学研究 01-26
- 农业微生物学国家重点实验室召开发展研讨会 01-26
- 图书馆召开教代会落实事业发展“十四五”规划 01-26
- 肖菊华副省长一行来校看望慰问寒假留校学生 01-26
- 我校研究团队揭示油菜杂◣交种的染色质三维结构特征 01-25
高考招生
- 2017年华中农业大学♀普通本科招生章程 08-05
- 2018年华中农业大学普通本科招生章程 08-05
- 华中农业大学2015年全日制普通本科招生章〇程▲ 08-05
- 华中农业大学普通本科招生章程(2016年) 08-05
- 华中农业大学2013年全日制▓普通本科招生章程 08-05
- 华中农业大学2014年全日制普通本科招生章程 08-05
- 华中农业大学2012年全日制普通本科招生章程 08-05
- 华中农业大学2008年全日制普通本科招生章程 08-05
- 华中农业大学2009年全日制普通本科招生章程 08-05
- 华中农业大学2007年全日制普通本科招生章程 08-05